What if Body and Mind were never separate concepts?
Be the buddy to your Body
Your body was designed to move.

Fitness
Just like food and water are essential to your body's functioning, so too is the movement your body needs to thrive. Regular exercise is essential for a long and healthy life. It strengthens your heart, improves brain function, and enhances overall well-being. By incorporating physical activity into your daily routine, you can reduce stress, improve sleep quality, boost your mood, and increase your lifespan.
Working with a personal trainer can increase your fitness level by up to 57%.
*Source: Journal of Sports Science and Medicine
Why can Fit Buddy be a perfect fit for you:
- A Fitness program tailored just for you: designed specifically to meet your unique goals.
- No One-Size-Fits-All: every individual is different, and your plan will reflect that.
- Anytime, Anywhere: work out whenever and wherever it suits you.
- Movement Analysis: we'll assess your current fitness level to ensure your plan is effective.
- Ongoing Support: receive guidance and motivation throughout your fitness journey.

Diet
You are what you eat. The foods you choose fuel both your body and mind. It's your responsibility to provide your body with the high-quality nutrients it needs. Invest in your health and longevity today and reap the rewards for decades to come.
Clinical trial on 415 people found that those who met with a nutrition coach virtually or in person lost significantly more weight than those who went about their weight loss solo.
*Source: https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1108660#t=article
Why can a Nutrition Coach be a perfect fit for you?
A Nutrition coach with a personalized plan: tailored to your unique needs, eating habits & limitations.
Bye, bye disposable solutions: learn how to make sustainable lifestyle changes.
Where you can’t. Expert Buddy can: we're here to guide you every step of the way.
Know, understand, and do it: gain valuable education about healthy eating.
Reach your true potential: improve your overall well-being and health.

Supplement
Even with a good fitness routine and a healthy diet, it can sometimes be difficult to get all the nutrients your body needs. The right supplements can help fill in the gaps and boost your health from optimal to full potential.
A recent study has shown supplementing with Nicotinamide, and Resveratrol may reverse age-related decline, and extend lifespan by up to 25%.
*Source: https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9861325/
How the right supplements complement your well-being:
Bridging Nutritional Gaps: high-quality supplements can help fill these gaps, ensuring your body receives the essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants it needs.
Targeted Support: the right combination of supplements can provide targeted support for specific health concerns.
Enhanced Performance: High-quality supplements help to optimize athletic performance, recovery, and overall vitality.
Antioxidant Protection: Supplements containing powerful antioxidants help neutralize harmful free radicals and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.
Long-Term Health Investment: By prioritizing your nutritional needs, you are supporting a healthier, more vibrant life and, in this way, increasing your life span.
Be the guru to your Mind
Explore the space beyond relaxation. Meditation is a more powerful tool for overall health and well-being than you can imagine.
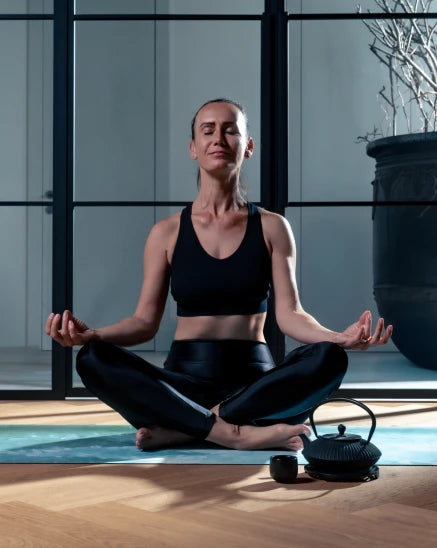

Meditation
Practicing meditation regularly enhances concentration, improves attention span, reduces symptoms of anxiety and depression, improves sleep, helps to lower cortisol levels that are responsible for stress, and enhances immune function.
Approximately 200-500 million people engage in meditation worldwide.
*Source: (Rakicevic, 2021)
Why does meditation enhance well-being?
Stress Reduction: regular practice can lower cortisol levels, the stress hormone, promoting a calmer and more relaxed state of mind.
Mental Clarity: enhances focus and concentration. By calming the mind, you can improve your ability to think clearly, make decisions, and learn new information.
Emotional Balance: helps to regulate emotions, leading to greater emotional stability. It reduces feelings of anger, frustration, and sadness, promoting a more positive outlook on life.
Physical Health Benefits: Regular meditation lowers blood pressure, reduces heart rate, and boosts the immune system. It can also alleviate chronic pain and improve sleep quality.
Spiritual Growth: connect with your inner self and develop a greater sense of awareness and compassion.
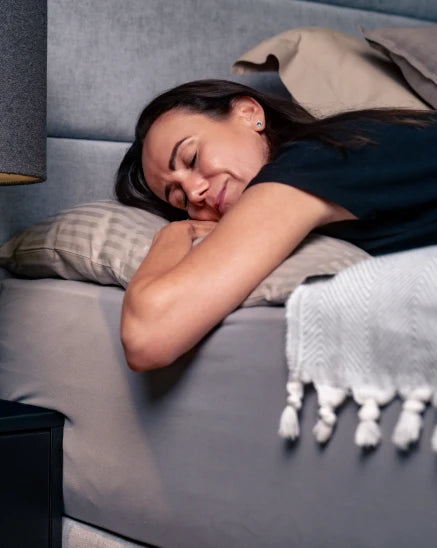

Sleep
Good sleep plays a crucial role in physical health, aiding in cell repair. Poor sleep can disrupt metabolism, leading to weight gain, insulin resistance, and other health issues. Prioritize sleep by creating a calming bedtime routine, ensuring a comfortable sleep environment that limits screen time before bed.
Up to 75% of older adults experience symptoms of insomnia.
*Source: https://www.sleepfoundation.org/how-sleep-works/sleep-facts-statistics
Why is sleep an integral part of overall health?
Boosts Cognitive Function: sleep is essential for cognitive function, including memory. It helps consolidate memories and enhances brain function.
Regulates Mood: Adequate sleep helps regulate mood and emotions. It can reduce feelings of anxiety, depression, and irritability, promoting a positive mental outlook.
Strengthens Immune System: During sleep, the immune system produces cytokines, which help fight infection and inflammation. Sufficient sleep helps strengthen the immune system, making you less susceptible to illness.
Maintains Metabolic Health: Inadequate sleep can disrupt these hormones, leading to weight gain, insulin resistance, and other metabolic disorders.
Promotes Physical Health: It helps repair tissues, build muscle, and heal wounds.
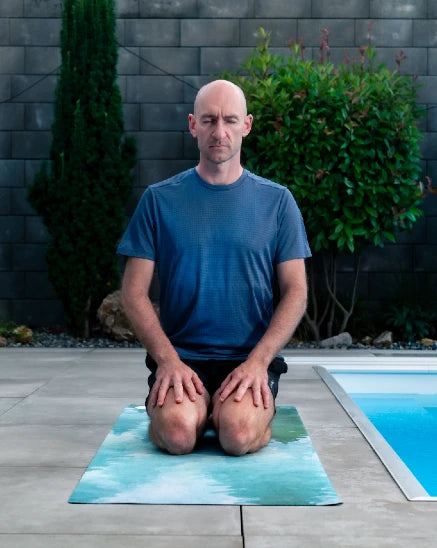

Cold & Breath
Discover the benefits of cold therapy with the instructor and author of the book "Cold Therapy: A Frosty Guide for Those Who Want to Dive into the Secrets of Cold Adaptation." For many years, he has been leading expeditions to Mountains in shorts alongside the book's co-author, Veronika Allister. He also conducts group sessions and provides cold therapy experiences for corporate teams.
Take off that coat, you'll get sick. (Wim Hof)
Transform your body with cold therapy:
Enhanced Energy and Focus: Experience increased alertness and reduced brain fog.
Accelerated Recovery: Recover faster from workouts and reduce muscle soreness.
Boosted Mood: Combat stress and anxiety, improve mental clarity and emotional balance.
Optimized Sleep: Improve sleep quality and duration for a more restful night's sleep.
Strengthened Immune System: Support your body's natural defenses against illness.
Our approach to breathwork is based on personal experiences and the latest scientific knowledge. It combines traditional practices such as Indian pranayama, the Chinese qigong, and modern systems like the Oxygen Advantage, as well as insights from authors and instructors like Dr. Belisa Vranich and James Nestor.
Before you try to control the world, control your breath. (Eastern proverb)
Experience the transformative power of breath therapy:
Boosted Energy Levels: Feel more energized and alert throughout the day.
Enhanced Focus and Mental Clarity: Improve your concentration and cognitive function.
Reduced Stress and Anxiety: Calm your mind and reduce feelings of stress and anxiety.
Improved Sleep Quality: Fall asleep faster and wake up feeling refreshed.
Enhanced Physical and Mental Recovery: Recover faster from workouts and reduce muscle soreness.
It was very important to us that our first product be formulated with the most researched, and cutting edge ingredients available on the market. AEON was created to be an all-in-one longevity focused supplement. Each compound is carefully chosen for its stand-alone benefits as well as its synergistic ones paired with the other 10.
— Tomas NetrvalCo-founder
The molecule responsible for aging
Imagine your body as a factory. To keep the factory running, it needs fuel. NAD+ is like that fuel for your body's cells.
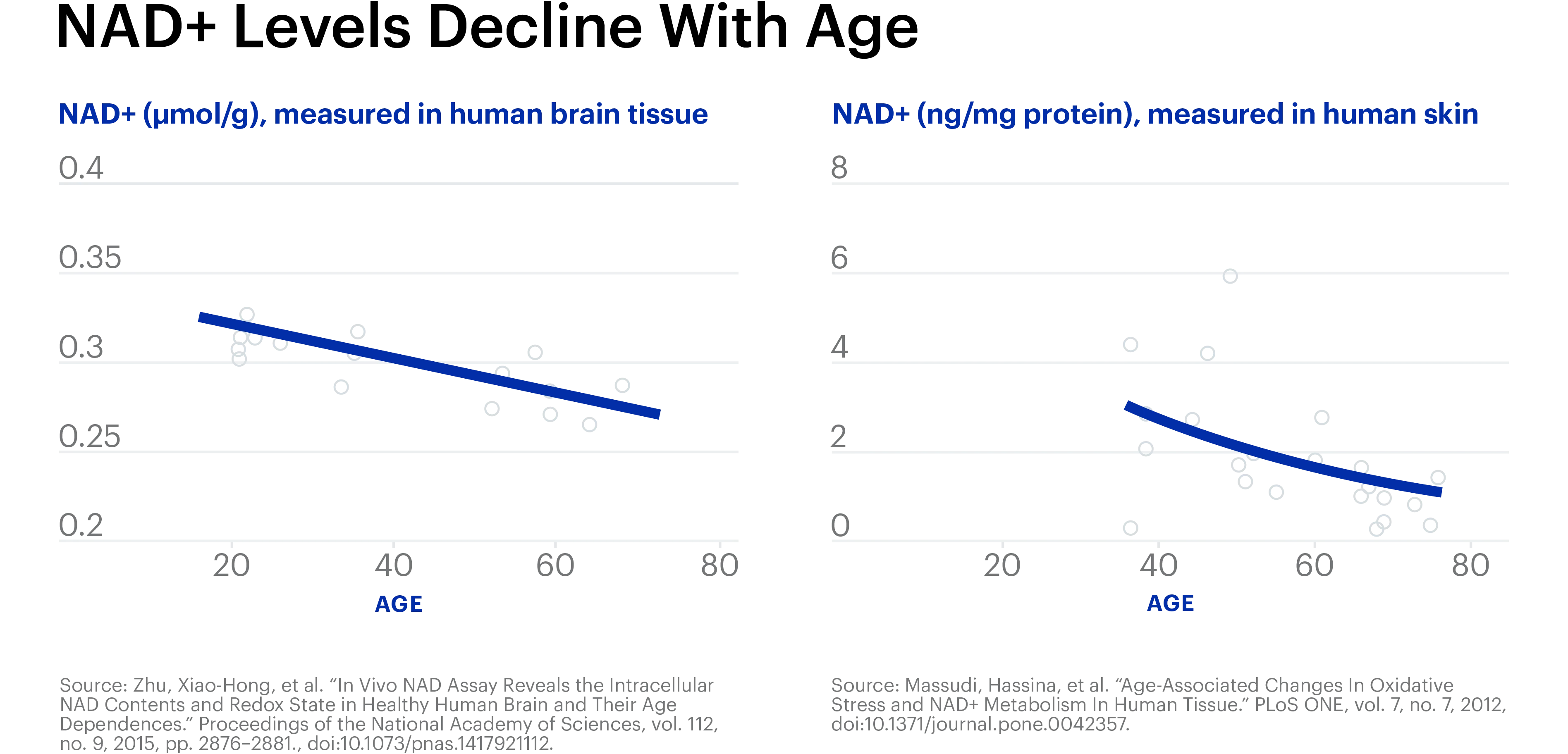
NAD+ is found in every cell in your body and is essential for creating cellular energy and maintaining cellular health. Levels of this critical molecule correlate with health status in aging. Its levels naturally decline with age, contributing to many age-related diseases.
What is NAD+?
NAD+ is found in every cell in your body and is essential for creating cellular energy and maintaining cellular health. Levels of this critical molecule correlate with health status in aging. Its levels naturally decline with age, contributing to many age-related diseases.
Why do NAD+ levels decline with age and when?
NAD+ levels usually decline gradually after age 30 and become more significant in people over 50 due to decreased production and increased consumption within the body. As we age, the enzymes responsible for NAD+ synthesis become less efficient, and there's a rise in activity of enzymes like CD38 that degrade NAD+, often due to factors like chronic inflammation and DNA damage. Lower NAD+ levels can lead to reduced cellular energy, impaired DNA repair, and other age-related health issues.
Poor diet, lack of exercise, and chronic stress also contribute to NAD+ decline as well as in response to stressors on your body, like alcohol consumption, sun exposure and lack of sleep.
What are the consequences of low NAD+ levels?
Low levels of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) can have several adverse effects on the body due to its central role in numerous cellular processes. Here are some of the consequences associated with reduced NAD+ levels:
- Decreased Energy Production: NAD+ is essential for cellular respiration, specifically in the processes of glycolysis and the Krebs cycle, which generate ATP—the primary energy currency of the cell. Low NAD+ levels can lead to reduced ATP production, resulting in fatigue and decreased cellular function
- Impaired DNA Repair: NAD+ is a critical substrate for enzymes like PARPs (poly ADP-ribose polymerases) that are involved in DNA repair mechanisms. Insufficient NAD+ can hinder the repair of damaged DNA, leading to genetic instability, which is associated with aging and an increased risk of diseases like cancer.
- Metabolic Dysregulation: NAD+ plays a significant role in metabolic pathways that regulate glucose and lipid metabolism. Low levels can contribute to metabolic disorders such as insulin resistance, obesity, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Reduced Sirtuin Activity: Sirtuins are a family of NAD+-dependent enzymes that regulate aging, inflammation, and stress resistance. Decreased NAD+ impairs sirtuin function, potentially accelerating aging processes and increasing susceptibility to age-related diseases.
- Neurodegeneration: Adequate NAD+ levels are important for neuronal health. Reduced NAD+ has been linked to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's, possibly due to impaired energy metabolism in neurons and increased oxidative stress.
- Weakened Immune Function: NAD+ influences immune cell function and the body's inflammatory responses. Lower levels may impair the immune system's ability to combat infections and manage inflammation effectively.
- Increased Oxidative Stress: NAD+ is involved in redox reactions that help neutralize free radicals. A deficiency can lead to an imbalance, causing cellular damage from oxidative stress.
- Mitochondrial Dysfunction: NAD+ is crucial for mitochondrial health. Reduced levels can impair mitochondrial function, leading to decreased energy production and increased production of reactive oxygen species.
- Cellular senescence: NAD+ is involved in regulating cellular senescence, a process in which cells stop dividing and become less functional. Premature cellular senescence is leading to tissue aging and decline.
- Increased risk of chronic diseases: Low NAD+ levels have been linked to an increased risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic disorders.
Maintaining adequate NAD+ levels is important for overall health, especially as natural levels tend to decline with age. Research is ongoing to explore interventions—such as NAD+ precursors like nicotinamide riboside and nicotinamide mononucleotide—that may help boost NAD+ levels and mitigate these adverse effects.
How can increasing NAD+ levels slow down aging?
There are several ways to maintain or boost NAD+ levels, but only NAD+ precursor supplementation has been clinically proven to safely and sustainably increase NAD+ levels. These precursors, nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN), are key ingredients in our NR and NMN supplements.
Engaging in exercise may help sustain NAD+ levels. Research published in Nature Aging examined metabolites in muscle tissue from both younger and older adults. The findings revealed that older adults who exercised vigorously had NAD+ levels comparable to those of the younger group. Since this study focused solely on muscle tissue, additional research is needed to understand how exercise affects NAD+ levels throughout the entire body.
Regarding dietary sources, as previously mentioned, foods contain trace amounts of NAD+ precursors. Small amounts of NMN are present in vegetables like broccoli, cucumber, and cabbage, as well as in some fruits. NR can also be found in foods, especially milk, but studies indicate that the quantities are in the low micromolar range—meaning they are quite minimal.
What is the current state of research on NAD+ and aging?
A recent study by researchers at the University of New South Wales has revealed a significant connection between aging and NAD+ levels. They found that NAD+ levels can decline by up to 50% between the ages of 40 and 60.
A paper published in Translational Medicine of Aging suggests that boosting NAD+ levels could be a powerful strategy for combating the effects of aging. The researchers state that "NAD+ replenishment may serve as a potential therapeutic strategy for aging and multiple conditions.
This groundbreaking research indicates that supplementing with NAD+ could potentially slow down certain aspects of the aging process. Fortunately, there are several NAD+ supplements available on the market to help you support your body's natural functions and maintain optimal health.
Are there promising areas of research or development?
In recent years, NAD+ has emerged as a prized molecule in scientific research due to its central role in essential biological functions. The scientific community is investigating how NAD+ contributes to notable health benefits observed in animal studies, with hopes of translating these findings to humans. So, what makes NAD+ so crucial? In essence, it acts as a coenzyme or "helper" molecule, binding to other enzymes to facilitate molecular reactions.
However, the body's supply of NAD+ is not endless; it actually declines with age. The rich history of NAD+ research and its growing significance have opened the floodgates for scientists to explore ways to maintain and enhance NAD+ levels.